
UN: The situation of pregnant women at the Islam Qala border is alarming

Women Activists: Forced Deportation of Migrants Amounts to “Silent Death”

Hiring of Illegal Afghan Migrants in Tehran’s Labor Market Banned

Malala Yousafzai: Supporting Women’s Sports in Afghanistan is a Form of Resistance

Amnesty International: World Confused by Afghanistan’s “Catastrophic Situation”

UN: The situation of pregnant women at the Islam Qala border is alarming

Women Activists: Forced Deportation of Migrants Amounts to “Silent Death”

Hiring of Illegal Afghan Migrants in Tehran’s Labor Market Banned

Malala Yousafzai: Supporting Women’s Sports in Afghanistan is a Form of Resistance

Amnesty International: World Confused by Afghanistan’s “Catastrophic Situation”
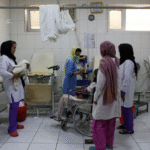
UN: 400 Health Centers Shut Down in Afghanistan

UN: The situation of pregnant women at the Islam Qala border is alarming

Women Activists: Forced Deportation of Migrants Amounts to “Silent Death”

Hiring of Illegal Afghan Migrants in Tehran’s Labor Market Banned

Malala Yousafzai: Supporting Women’s Sports in Afghanistan is a Form of Resistance

Amnesty International: World Confused by Afghanistan’s “Catastrophic Situation”

UN: 400 Health Centers Shut Down in Afghanistan

UN: The situation of pregnant women at the Islam Qala border is alarming

Women Activists: Forced Deportation of Migrants Amounts to “Silent Death”

Hiring of Illegal Afghan Migrants in Tehran’s Labor Market Banned

Malala Yousafzai: Supporting Women’s Sports in Afghanistan is a Form of Resistance

Amnesty International: World Confused by Afghanistan’s “Catastrophic Situation”

UN: 400 Health Centers Shut Down in Afghanistan

UN: The situation of pregnant women at the Islam Qala border is alarming

Women Activists: Forced Deportation of Migrants Amounts to “Silent Death”

Hiring of Illegal Afghan Migrants in Tehran’s Labor Market Banned

Malala Yousafzai: Supporting Women’s Sports in Afghanistan is a Form of Resistance

Amnesty International: World Confused by Afghanistan’s “Catastrophic Situation”

UN: 400 Health Centers Shut Down in Afghanistan

One Year after the Herat Earthquake; Victims Complain About Neglect and Their Problems
A year after the deadly and continuous earthquakes in Herat province, western Afghanistan, many families and individuals who lost family members and property, as well as their homes being destroyed, are criticizing the lack of support from international organizations and the interim government of Afghanistan. The earthquake victims state that they still do not have access to basic living necessities and are suffering greatly from their current conditions. They cite the lack of adequate shelter, insufficient healthcare facilities, absence of educational centers, and limited access to drinking water as their main challenges, calling for assistance from international organizations, national traders, and the government. Zalmai Farooqi, a resident of Nayeb Rafi village in the Zenda Jan district of Herat, is 35 years old and had four children. He lost two daughters in the earthquake, aged between 10 and 15 years. The village where Zalmai lived was nearly flattened by the continuous earthquakes. With a heavy voice and choked throat, Zalmai told the media that he is still in shock and has not been able to forget the immense suffering that the earthquake has imposed on them. He says, "I see my daughters almost every night in my dreams, and this has become a painful nightmare for me." He stated that he lost his home and all his belongings in the earthquake. Criticizing the organizations and government, he mentioned that many promises were made to them after the earthquake, but few have been fulfilled. As a result, even after a year, they continue to struggle with numerous problems. He also harshly criticized the houses that were constructed for him, emphasizing: "The houses they built for us are just shelters. There are no walls around them, no water, and no electricity. They don’t even have a toilet. Winter is approaching, and we cannot afford to build walls around our homes. Additionally, the prices of construction materials have skyrocketed." Government and Organizations' Promotional Perspective on the Victims Shah Mahmood, another victim of the devastating Herat earthquake, shared his struggles with the media outlet Goharshad, stating, and “We walk half an hour on foot we are facing many challenges. However, the government and international organizations are completely indifferent to our problems. They are only focused on publicity and baseless activities, neglecting the essential needs of the people." Shah Mahmood expressed that they are still confronted with numerous issues. He mentioned that the houses built for them by the government and some traders lack surrounding walls, creating significant problems for families both during the day and especially at night. He noted that for several months, the people of this village have received no assistance from the interim government or aid organizations, and they are facing severe food and health challenges. Shah Mahmood criticized the aid organizations for "turning their backs" on earthquake victims in Herat, showing no concern for their basic needs. This comes in the wake of a powerful earthquake measuring 6.3 on the Richter scale that struck the Zenda Jan district of Herat on October 7 last year. In the following days, similar earthquakes once again shook Zenda Jan and other districts in Herat, leaving widespread destruction and casualties in their wake. According to international organizations, approximately 1,500 people lost their lives in these earthquakes, over 2,600 were injured, and thousands of homes were destroyed. The occurrence of these earthquakes has left thousands homeless and displaced. After these earthquakes, the United Nations, aid organizations, and the current government repeatedly announced plans to assist victims and construct shelters for them; however, it seems that these efforts have not been able to meet their extensive needs. 96,000 Vulnerable Children Affected by the Earthquake UNICEF, the United Nations Children's Fund, recently released a report stating that one year after the earthquake in Herat, 96,000 earthquake-affected children in the province remain at risk and require further support. The report highlighted that most victims of this disaster were children and women, emphasizing the need for increased assistance for children. UNICEF stressed that the situation of earthquake victims in western Afghanistan is dire. The report continued to state that in the year following the disaster, UNICEF prioritized rebuilding damaged water supply systems, restoring classrooms, and ensuring uninterrupted health and nutrition services for children and women. The report indicated that over one million people have accessed healthcare through medical teams supported by UNICEF, including 400,000 children under five years old. UNICEF restored access to clean drinking water for 21,600 individuals and installed sanitation facilities for 25,000 people. The report concluded: "Children cannot thrive without reliable essential services, especially climate-resilient water systems. In areas like Herat, which have been severely affected by drought and are still recovering from earthquakes, we must ensure that communities have access to safe drinking water."

The Narrative of Women; I Did Not Experience Childhood, Nor Life, I Am Just Alive
Author: Sara Karimi My name is Maryam. I am thirty-five years old, or maybe even older. To be honest, I don't know exactly how old I am. My birth certificate has my birth year wrong, and I have never had the time to think about the numbers on that paper. What I do know is that my life ceased to be a life the day I turned fifteen. At fifteen, I was married off. Not in a dazzling white dress, nor with a grand ceremony. It was just a simple night when my mother oiled my hair, draped a white scarf over my head, and said, "My daughter, may God give you strength; you are now a wife, and you will be happy." I said nothing. My heart was full, but my tongue was tied. I was scared, but not of my husband; I was afraid of a future I did not know. My husband was thirty-one years old. My father had said, "He is a hardworking man and believes in God; he doesn’t have a wife; his first wife died." That night, there was only the sound of drums and circular instruments and the heavy gaze of female relatives whispering under their breath. The day after that night, I was no longer a girl. My husband's home was a cold and silent place. The walls were made of mud, and the carpets were old. My husband did not talk much. He would sleep without a word at night and leave for work early in the morning. I was left alone with my fears and unanswered questions. A few months later, I found out I was pregnant. My body was still that of a child, but another child was growing inside me. Deep down, rather than feeling the joy of becoming a mother, I was terrified. My delivery was difficult. I gave birth at home with the help of a neighbor woman. My cries were swallowed by the walls. There was no doctor, no medicine, no one—just me and God. When my newborn was placed in my arms, my heart trembled. This tiny being was mine, yet I felt a strange sensation—a feeling of being lost. I still didn’t know what I was doing or who I was meant to be, yet now I had to be a mother. Years passed. I became pregnant one after another. I gave birth to six children. Each time I delivered, it felt like I left a part of myself behind. My body deteriorated, and so did my spirit. There were nights when I couldn't sleep from pain, but in the morning, I had to wake up again, cook food, and gather the children. At first, my husband worked as a construction laborer. Sometimes he would sweat in people’s gardens. But life became harder. One day he fell from the second floor of a building. From that day on, he was never the same man again. It wasn't that his injury was severe, but the blow to his head seemed to change his mind. He became more irritable day by day. Sometimes he would yell for no reason; sometimes he would pound his fists against the wall. The children were scared. So was I. Then gradually he became quiet. He would sit in a corner and just stare at one point. Now it has been years since he has spoken or worked. Sometimes his lips move as if he is praying under his breath. Occasionally at night he has nightmares, wakes up screaming and crying like a child. I try to calm him down while I myself am shattered into a thousand pieces. Who bears the household expenses? Me. But I have no skills. I have never been to school. I don't know how to sew, do math, or read properly. The only thing I knew how to do was survive, and even that I did well. Now I collect stale bread. Sometimes I clean houses for people in exchange for a piece of bread or a few Afghanis. My children... what can I say? Three of them do not go to school. Either we have no money or no shoes. My eldest, Ahmad, is ten years old. In the mornings, he goes out with a heart full of hope to collect garbage: metal, plastic bags, bottles—anything someone has thrown away. His hands are wounded, but he smiles when he finds even 20 Afghanis. My daughter, Zainab, is eight years old. She has no doll. She wants to become a teacher, but I don’t know if I will even be alive by then! I'm always scared someone will come to ask for her hand in marriage, just like they did for me. Should I stop it? What can I do? How can I keep her safe? With her empty stomach? With her torn clothes? Every night we go to bed with half-empty stomachs. Sometimes for dinner there is only stale bread and boiling water. If a neighbor shows mercy and gives us something, that day feels like a celebration. My children have learned not to ask for anything. They have learned silence. My husband now often doesn’t know where he is. Sometimes he calls out his dead mother’s name; sometimes he addresses our youngest son as “father.” My heart aches for him—not because I loved him, but because he was once a person who suffered until his mind broke down. Now he seems like a corpse that breathes. Who am I? A woman who did not experience childhood, nor youth, nor even motherhood properly. Just a burden on her own shoulders—always running but never reaching anywhere. Sometimes at night when everyone is asleep, I sit in a corner and think—about the past, about the day when I played in the dirt in our yard, about when I wanted to become a painter. Now my hands are only filled with scars. I have no notebook or pen—just a heart. I asked God to let me die. Several times. But then I remembered, if I die, what will happen to the children? Who will soak their dry bread? Who will touch their foreheads when they have a fever? I have to stay. For them. Even if I am no longer myself. I am just alive. I have not lived. From the age of fifteen until today, I have only survived.

Author: Sara Karimi My name is Maryam. I am thirty-five years old, or maybe even older. To be honest, I don't know exactly how old I am. My birth certificate has my birth year wrong, and I have never had the time to think about the numbers on that paper. What I do know is that my life ceased to be a life the day I turned fifteen. At fifteen, I was married off. Not in a dazzling white dress, nor with a grand ceremony. It was just a simple night when my mother oiled my hair, draped a white scarf over my head, and said, "My daughter, may God give you strength; you are now a wife, and you will be happy." I said nothing. My heart was full, but my tongue was tied. I was scared, but not of my husband; I was afraid of a future I did not know. My husband was thirty-one years old. My father had said, "He is a hardworking man and believes in God; he doesn’t have a wife; his first wife died." That night, there was only the sound of drums and circular instruments and the heavy gaze of female relatives whispering under their breath. The day after that night, I was no longer a girl. My husband's home was a cold and silent place. The walls were made of mud, and the carpets were old. My husband did not talk much. He would sleep without a word at night and leave for work early in the morning. I was left alone with my fears and unanswered questions. A few months later, I found out I was pregnant. My body was still that of a child, but another child was growing inside me. Deep down, rather than feeling the joy of becoming a mother, I was terrified. My delivery was difficult. I gave birth at home with the help of a neighbor woman. My cries were swallowed by the walls. There was no doctor, no medicine, no one—just me and God. When my newborn was placed in my arms, my heart trembled. This tiny being was mine, yet I felt a strange sensation—a feeling of being lost. I still didn’t know what I was doing or who I was meant to be, yet now I had to be a mother. Years passed. I became pregnant one after another. I gave birth to six children. Each time I delivered, it felt like I left a part of myself behind. My body deteriorated, and so did my spirit. There were nights when I couldn't sleep from pain, but in the morning, I had to wake up again, cook food, and gather the children. At first, my husband worked as a construction laborer. Sometimes he would sweat in people’s gardens. But life became harder. One day he fell from the second floor of a building. From that day on, he was never the same man again. It wasn't that his injury was severe, but the blow to his head seemed to change his mind. He became more irritable day by day. Sometimes he would yell for no reason; sometimes he would pound his fists against the wall. The children were scared. So was I. Then gradually he became quiet. He would sit in a corner and just stare at one point. Now it has been years since he has spoken or worked. Sometimes his lips move as if he is praying under his breath. Occasionally at night he has nightmares, wakes up screaming and crying like a child. I try to calm him down while I myself am shattered into a thousand pieces. Who bears the household expenses? Me. But I have no skills. I have never been to school. I don't know how to sew, do math, or read properly. The only thing I knew how to do was survive, and even that I did well. Now I collect stale bread. Sometimes I clean houses for people in exchange for a piece of bread or a few Afghanis. My children... what can I say? Three of them do not go to school. Either we have no money or no shoes. My eldest, Ahmad, is ten years old. In the mornings, he goes out with a heart full of hope to collect garbage: metal, plastic bags, bottles—anything someone has thrown away. His hands are wounded, but he smiles when he finds even 20 Afghanis. My daughter, Zainab, is eight years old. She has no doll. She wants to become a teacher, but I don’t know if I will even be alive by then! I'm always scared someone will come to ask for her hand in marriage, just like they did for me. Should I stop it? What can I do? How can I keep her safe? With her empty stomach? With her torn clothes? Every night we go to bed with half-empty stomachs. Sometimes for dinner there is only stale bread and boiling water. If a neighbor shows mercy and gives us something, that day feels like a celebration. My children have learned not to ask for anything. They have learned silence. My husband now often doesn’t know where he is. Sometimes he calls out his dead mother’s name; sometimes he addresses our youngest son as “father.” My heart aches for him—not because I loved him, but because he was once a person who suffered until his mind broke down. Now he seems like a corpse that breathes. Who am I? A woman who did not experience childhood, nor youth, nor even motherhood properly. Just a burden on her own shoulders—always running but never reaching anywhere. Sometimes at night when everyone is asleep, I sit in a corner and think—about the past, about the day when I played in the dirt in our yard, about when I wanted to become a painter. Now my hands are only filled with scars. I have no notebook or pen—just a heart. I asked God to let me die. Several times. But then I remembered, if I die, what will happen to the children? Who will soak their dry bread? Who will touch their foreheads when they have a fever? I have to stay. For them. Even if I am no longer myself. I am just alive. I have not lived. From the age of fifteen until today, I have only survived.

Author: Sara Karimi In a dusty alleyway of Kabul, a girl named Nadia lived with big dreams and a heart full of sorrow. From a young age, she knew that education and university were the only way to escape poverty, unemployment, family struggles, discrimination, and social inequalities. Nadia was born into a humble and poor family in a hidden corner of Kabul, where girls were mostly raised to do household chores and get married rather than pursue academic dreams. But Nadia thought differently, imagined differently, and saw the world through a unique lens. She attended school despite being criticized for being a girl. Many told her that education was unnecessary for girls, that they should stay at home and learn the customs of marriage and domestic life. Yet, from childhood, Nadia was determined to prove that girls could have big dreams, create change, and transform society. Her teachers recognized her as a hardworking and intelligent student. She excelled in all her subjects, and some of her classmates envied her. At home, her parents encouraged her, especially her father—a simple cart vendor—who believed in his daughter’s bright future. He would always say, "The world does not belong only to men. My daughter must become someone who brings great change." After years of struggle and overcoming social restrictions, Nadia finally succeeded in passing the university entrance exam. She was admitted to Kabul University to study economics, her passion. Her first days at university felt like a dream. With bright eyes and a heart full of hope, she attended classes enthusiastically. She was known among her classmates not only for her academic excellence but also for her determination, mindset, and perseverance. But her happiness did not last long. In the year when she was at the peak of her success, everything in Afghanistan changed. Once again, sorrow and pain took over her heart. The ruling regime returned to power, and one by one, universities and schools for girls were shut down. Nadia, who had fought for years to reach this moment, now faced an insurmountable wall of oppression and restrictions. Instead of sitting in classrooms and learning, she was forced to stay at home, reminiscing about her bright past and shedding tears over lost opportunities. Days felt endless, blending into nights. Nadia was confined to her home, but she never lost hope. She vowed that as long as she breathed, she would never abandon her pursuit of knowledge and dreams. At night, when her family slept, she would take out her books and study under the dim light of her lamp—the only source of brightness in her dark world. Books became her closest companions, giving her hope that maybe, one day, she could return to university. "The light of knowledge, passion, and effort still shines in my dark world, and hope remains alive in my heart," she told herself. Even when she saw the sorrow in her parents' eyes, knowing they felt helpless about her future, she remained strong. She believed that within every hardship, an opportunity was hidden. But sometimes, she wondered—would the world ever make enough space for a girl's dreams? One difficult day, a knock on the door shattered the silence. Nadia rose from her books, hearing footsteps approaching. The voices of men grew louder as they neared her home. Her heart pounded. She knew the authorities had come. In that moment, memories of her university days flashed before her eyes like a film. Fear gripped her, but deep inside, something told her she must keep going, even if she could never return to her studies. The regime's forces entered their home, bringing nothing but threats and fear. Their orders were clear: "Girls must stay at home and do household chores. There is no place for you in schools and universities anymore." At that moment, for the first time, Nadia told herself, "Even if I cannot study in this closed world, no one can take my dreams away from me. As long as hope lives in my heart, I am still free." That night, as she sat with her family, lost in memories, she made a silent promise: if the world ever gave her a chance, she would fight for all the girls in Afghanistan who were deprived of education. Nadia may not have returned to university that night, but her spirit and hope remained alive—in the hearts of all the girls who longed for freedom and education. And someday, in an unknown future, perhaps from behind these towering walls of oppression, the voices of girls like Nadia will rise—voices that the world will finally hear.

On one of the cold autumn days in a corner of Kabul, there lived a girl named Parisa. She was 12 years old and, due to poverty and economic difficulties, had to go out to the streets early in the morning to sell flowers. Every day, Parisa would take a small basket filled with wildflowers she gathered from around the city to the central square. Among the flowers, she found beauty and hope, and by selling them, she tried to improve her family's situation. Parisa's father, who had previously worked as a construction worker, had become unemployed due to an injury. Her mother was also seriously ill and unable to work. Because of these responsibilities, Parisa never had the chance to go to school and continue her education. She kept all her dreams hidden in her heart: "Dreams of education, freedom, and a better life." One day, Parisa decided to sell her flowers at a lower price to attract more customers. In the following days, with tireless effort, she brought her flowers to the people. However, no one appreciated them, and most of the time she returned home empty-handed. One night, when Parisa returned home, she noticed that her mother's condition had worsened. She sadly approached her mother's bedside and realized they could no longer afford medicine. Tears welled up in her eyes as she wished she could bear the pain her family was enduring. The next morning, with a broken heart, Parisa went back to the streets. This time instead of selling flowers, she visited shops and asked if they could help her in any way. Wherever she went, she faced indifference and coldness. Exhausted and hopeless, Parisa sat on the side of the street, looking with tear-filled eyes at the life that hurt her every second as it passed by. That evening, when Parisa returned home, her mother was no longer by her side. Her death shattered Parisa's heart and left her in a world of darkness. Not only did she no longer bear the responsibility of her family, but now she was alone and vulnerable in a harsh and merciless world. However, Parisa decided to continue living. In memory of her mother, she persevered in her efforts, hoping that one day she could change her life. Her heart was filled with sorrow, but with memories of her mother, she continued to gather flowers and move forward in life. Hope and love for life gave Parisa the strength to spread light wherever she went. Author: Mohammad Reza Ramez

Dark clouds have enveloped everything. It feels as if bullets and missiles are raining from the sky. My ears can no longer distinguish any other sound amidst the cacophony. Everyone is fleeing, but the destination is unclear. Some have rushed towards the metal birds (planes); the streams of water are now filled with blood. My eyes see not cars, but corpses, as if zombies have overtaken the world. I open my eyes and once again, it’s a nightmare! My forehead is drenched in sweat. My body is trembling. I don’t know when these nightmares will cease. For three years, they have stolen sleep from my eyes. This dream is pure reality that has slowly turned into a nightmare—untimely nightmares that escort me to the brink of death every night. For a long time now, these nightmares have become my nightly companions. During the day, I am silent, and at night, I am bound by this true nightmare. Hearing the sounds of phantom cries, which I find difficult to distinguish between sleep and wakefulness, I get out of bed. I wipe my sweaty forehead and follow the frequency of the crying outside; yes! I had guessed correctly—it was my sister’s voice. My unfortunate sister, trembling from the force of her sobs. Harsh and unsettling thoughts raced through my mind as I hurried to her. With a voice that seemed to rise from the depths of a well, filled with fear and anxiety, I asked her what had happened. With eyes sadder than ever, amidst her sobs, she said she had submitted a blank exam paper. And I, unable to even ask her why, because I know the reason for her actions. My unfortunate sister does not want to graduate from sixth grade so soon. She still wants to go to school, to learn, and she hasn’t yet let go of her love for school. The fear of never going back to school and not seeing her classmates again has consumed her like a parasite. I completely understand how this pain gnaws at her being. As I saw her, I momentarily returned to the past, to the days when I was sitting in a university classroom. I still remember that fateful day, the day when one of our professors entered the class along with our principal. I can still recall their sorrowful and mournful gaze. They wouldn’t lift their heads from the ground, as if they had committed a crime as grave as murder. Our principal avoided making eye contact with us, as if he feared what might happen if our eyes met. It was clear he had been crying, but he seemed unwilling to reveal the lingering lump in his throat. In a voice we had never heard before, he told us, “Due to an order we have received, you can no longer attend university and…” I never heard the rest of his words that day. As far as I remember, I felt as if someone had wrapped their hands around my throat and was trying to cut it with a dull knife. In that moment, even my breaths were not helping me; all I could hear was the sound of my classmates crying. Their wails still echo in my ears like the tolling of a death bell that has long been ringing. That day, I brought my half-dead body home. With my sister's voice, I return from the past to a present that bears no resemblance to life. My sister calls my name and asks how I am. With pain and tears still tracing her cheeks, she asks if I remember today. I tell her, “How can a person forget the day their soul died?” Today marks three years since the fall of Afghanistan. Today is exactly the day when misfortune was inscribed upon our fate. It’s the day we stopped wishing and started praying for death. It has been three years since my notebooks gathered dust, my pens wrote not a single word, and the lessons I struggled for months to learn have faded from memory. In these three years, I have lost everything I had; sometimes I think we all became ill overnight. Our spirits and minds are no longer healthy. I wish there were a psychologist to whom we could express the pains and lumps in our throats—the words that are slowly consuming our souls and bending our backs. I no longer feel alive; in these three years, I have died and come back to life a thousand times. If I were to forgive the whole world, I would never forgive those who caused me to be deprived of education, who made me feel worthless, separated me from society, and deprived me of my human rights. They have taken away rights that are mine and inflicted pains upon me during this time that can never be compensated. Author: MahNoor Roshan

The story begins with a 30-minute karate class on the balcony of her home in Peshawar, Pakistan. At that time, Nagara Shahin was an 11-year-old Olympic refugee, having spent most of her short life in exile and migration. Nagara fled Afghanistan with her parents in 1993 when she was just a baby. Her mother carried her for two days and nights while crossing mountains and passes. To pursue her beloved sport, Nagara faced numerous obstacles, from her first and last karate class to competing in judo at the Olympics as a member of the Olympic Refugee Team. Since 2022, this 31-year-old athlete has been living and training in Toronto, Canada. Nagara Shahin completed her education in Pakistan, where she endured harassment from men and bullying from her peers on her way to school. In an article published in *Life Toronto*, she recalls: “One day, an older man harassed my sister and me. He shouted at me and pushed me to the ground. I wanted to hit him with my fist, but I didn’t know how to do it.” Her mother told her she needed to learn to defend herself. The school she attended did not offer martial arts training, either in the regular curriculum or extracurricular activities. Through distant relatives, Nagara learned about a karate instructor nearby. Although the male instructor couldn't teach at the school, he could come to her home. Soon enough, Nagara began practicing on her aunt's balcony. She says, “My mother said this space could be provided by family, and you should use it as much as you can.” Before long, Nagara Shahin participated in local karate competitions. Her coach recognized her enthusiasm and skill and encouraged her to compete in judo. “My first coach told me, ‘You won’t learn to get up until you fall.’ This advice motivated me greatly during my childhood.” She also fondly remembers watching professional wrestling matches in America with her father, who was a wrestling enthusiast. Judo gave Nagara Shahin the confidence to find herself and enjoy life despite all the suffering and hardships of displacement and seeking asylum. According to a BBC news report, her coaches gradually began to recognize her skills. She reached a point where she trained with the national judo team of Pakistan but was unable to compete with them due to not having a Pakistani passport. In 2014, Nagara Shahin returned to Afghanistan and studied political science and public administration at the American University of Kabul. She also trained with the Afghan national team, and her male teammates welcomed her presence. As noted in *Life Toronto*, “During training, we were like a family, and they treated me like their sister.” She continued to train and compete, gaining significant attention as a female athlete in Afghanistan, which was somewhat unintentional. She told the BBC, “I faced immense cyber violence. This violence later turned into real harassment.” She recounted, “Several times, cars followed us. Once, a soda can was thrown at my mother, and I skillfully managed to save her.” In her first competition at the Tokyo Olympics, Nagara suffered a shoulder injury. In 2018, she left her homeland. She said, “I always say I became a refugee for the second time.” She went to Russia to continue her studies in entrepreneurship and international business. Unlike the warm welcome she received during training in Afghanistan, she couldn’t find a suitable group to train with in Russia. She spent a year training alone, which she describes as the bitterest period of her athletic career. In 2019, she met with a member of the International Judo Federation who suggested she join the Olympic Refugee Team. She qualified to participate in the 2020 Tokyo Olympics but was eliminated in her first match due to her shoulder injury. Until she completed her studies in Russia, the situation in Afghanistan had deteriorated significantly. Nagara said, "I was trapped." She returned to Pakistan but often stayed at home out of fear for her life. She faced severe attacks and criticism for not adhering to hijab regulations during competitions, which made her think more about her next steps. During this time, with the help of the Olympic Refuge Foundation and the UN Refugee Agency, she was given the opportunity to live and study in Canada. Nagara Shahin was accepted to continue her education in International Development in Toronto. She arrived in Canada in September 2022—a bittersweet moment for an athlete who has sought stability and peace across three different countries. It was in this Canadian city that her athletic life in judo was revitalized. In Paris, she is one of 37 athletes on the refugee team—a team that Nagara Shahin is proud to be a part of. Today (Saturday, August 20), she is set to step onto the mat once again and will compete for the first time in a mixed event representing the refugee team. Before the competitions, she told the International Judo Federation, "Team competitions are more exciting because I always look at my teammates, and I can't let them lose; that's why I fight for all of them." After the games, Nagara Shahin plans to declare Canada her home. She has now received permanent residency in Canada and hopes to one day be a supporter and helper for refugees like herself. Her mother and father are still in Pakistan and are happy that she has been able to realize her dream of participating in the Olympics. She says she relied on her family's support during the toughest times. "My sister always told me, 'I believe you will eventually reach your goal, and all these hard days will become memories that you can laugh about.'" "And now is the time when I can laugh about everything I've been through."
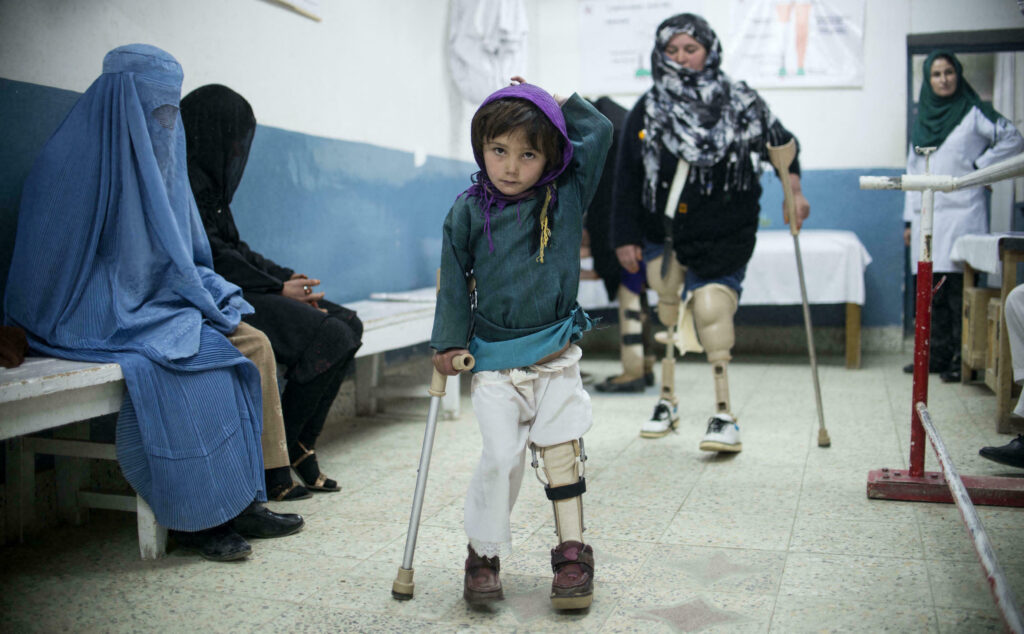
The Legacy of Decades of War in Afghanistan; Life-Destroying and Deadly Mines and Explosives
Author: Mahdi Mozaffari The prolonged and deadly wars in Afghanistan have left behind a bitter and dangerous legacy. Battlefields and residential areas of the country are filled with mines and explosive devices that endanger the lives of millions and continue to claim victims. According to reports from international organizations such as the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), "Afghanistan remains one of the most mine- and explosive-contaminated countries in the world." Millions of people in the country live near these hazardous remnants and constantly face the threat of explosions and death. This danger is particularly severe for children, who unknowingly play in these contaminated areas. Statistics published by the United Nations show that dozens of people in Afghanistan lose their lives or are injured every month due to mine and explosive detonations, with children making up the majority of victims. Such tragic incidents frequently occur across the country, serving as a grim reminder that the threat of mines and explosives remains ever-present, taking the lives of innocent people. Suspension of a Mine-Clearing Organization's Operations After returning to the White House, U.S. President Donald Trump suspended financial aid to various countries, including Afghanistan. This decision sparked multiple reactions at both international and domestic levels in Afghanistan. The interim government announced that due to the "suspension of these aids," "50 humanitarian organizations" in Afghanistan have ceased their operations. Among those affected, the suspension of aid has also impacted the mine-clearing sector, causing the shutdown of an organization in this field. The Norwegian People's Aid (NPA) recently announced that due to the "suspension of U.S. aid," it has halted its "mine-clearance activities in Afghanistan and 11 other countries worldwide." NPA stated that mine clearance falls under the U.S. security assistance program, historically receiving bipartisan support in the United States. The organization revealed that in 2024, it received nearly $41 million in funding from U.S. government agencies for its operations. NPA expressed hope that the new U.S. administration would continue its support, allowing the organization to resume its activities. It emphasized that mine clearance is an effective measure in reducing global poverty, enhancing security, and promoting economic development and stability. The organization warned that mines and other remnants of war pose a severe threat to people's lives, livelihoods, and post-conflict development. The suspension of mine-clearance activities could have irreversible consequences for the Afghan people and severely hinder efforts to clear the country of war remnants. UN Requires $21.9 Million for Mine-Clearing Operations The United Nations has requested $21.9 million in funding to continue mine-clearance operations in Afghanistan in 2025. This request, made by OCHA, aims to finance organizations involved in demining programs across the country. This appeal comes as Afghanistan's mine-clearance programs in 2024 faced severe funding shortages. According to OCHA, organizations in this sector received only 40% of their required budget, leading to the suspension of some operations. This financial shortfall has raised concerns about the future of mine-clearance efforts in Afghanistan, highlighting the serious challenges these programs face. Despite these difficulties, OCHA remains hopeful that donor countries will provide the necessary funds to support mine-clearance organizations in Afghanistan, ensuring the continuation of these crucial efforts. Sustained funding is essential for protecting civilians and preventing casualties from landmine explosions and unexploded ordnance. The Consequences of Mine-Contaminated Lands The failure to clear mine-contaminated lands in Afghanistan has devastating and far-reaching consequences for the country's people and society. This issue not only poses a significant threat to human life and health but also obstructs economic and social development as well as the reconstruction of damaged infrastructure. 1. Human Casualties and Physical Injuries: Landmines and explosive remnants of decades of war continue to claim innocent lives and cause irreparable physical harm. Children, farmers, and those living in mine-contaminated areas are at the highest risk. These casualties not only bring immense suffering to families but also place a heavy burden on the country's already struggling healthcare system. 2. Obstacles to Economic and Social Development: Mine-contaminated lands are unusable for agriculture and livestock farming, jeopardizing food security and exacerbating poverty and unemployment in rural areas. Furthermore, the presence of mines hinders the reconstruction of essential infrastructure such as roads, schools, and hospitals, slowing down Afghanistan's economic and social development. 3. Psychological and Social Issues: Living in mine-contaminated areas causes constant fear and anxiety, severely affecting people's mental health. This situation is particularly harmful to children, who face the risk of landmines while playing. Additionally, mines can force people to abandon their homes, leading to displacement and significant social and economic challenges. "Clearing Afghanistan's mine-contaminated lands is an urgent and vital necessity requiring serious attention and investment from the global community and the Afghan government. Until this issue is fully resolved, the Afghan people will remain at serious risk, and the country’s path to recovery and development will continue to face major obstacles."













